In this article, you will learn in details that what is a single plate clutch and multi plate clutch? Its types, construction and working, advantages and disadvantages.
Watch the video below to understand How does a CLUTCH work?
Table of Contents
What is Single Plate Clutch?
Single plate clutch has one clutch plate and works on the principle of friction. These are of two types: Helical spring type and Diaphragm spring type.
In helical spring-type clutches, the helical springs are used uniformly over the cross-sectional area of the pressure plate to exert axial force.
In diaphragm spring type clutch, diaphragm spring is used to exert axial force.
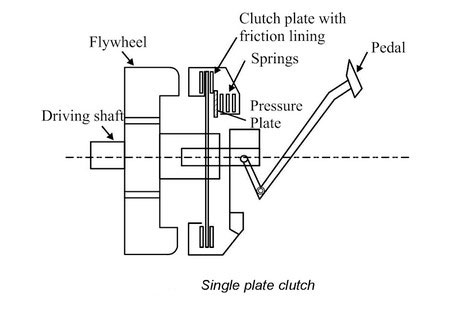
Construction and working of Single Plate Clutch.
Basically, the clutch needs three parts. These are the engine flywheel, a friction disc called the clutch plate, and a pressure plate.
A flywheel is a heavy disc with suitable width bolted to the end of crankshaft.
Friction disc is also called a clutch plate. It has friction lining on both sides of the friction plate.
The pressure plate is a disc; it engages with a clutch plate. When the engine is running, and the flywheel is rotating, the pressure plate also rotates as the pressure plate is attached to the flywheel.
The friction disc is located between these two. The clutch is released when the operator or driver has pushed down the clutch pedal.
This action forces the pressure plate to move away from the friction disc. There is now air gaps between the flywheel and the friction disc, and between the friction disc and the pressure plate. And no power can be transmitted through the clutch.
During the operation, when the driver releases the clutch pedal, power can flow through the clutch.
Springs mounted in between the clutch plate and pressure plate; it forces the pressure plate against the friction disc. This action clamps the friction disk tightly between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
Now, the pressure plate and friction disc rotate with the flywheel.
Advantages of Single Plate Clutch.
The main advantages of this clutch include its simplicity, easy gear changing, better heat dissipation from the single plate, smooth operation, and better load withstanding capacity.
Disadvantages of Single Plate Clutch.
The main drawback of this clutch is that its size is large and requires force to disengage the driving shaft from the driven shaft.
Types of Single Plate Clutch.
1. Helical Spring Type Single Plate Clutch.
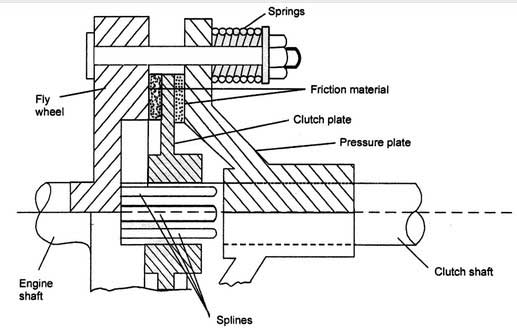
Below figure represents a single plate clutch of helical spring type. For simplicity sake, the clutch pedal and other links causing movement of pressure plate are not shown.
The clutch plate is mounted on the splined shaft and can move along the axis of the shaft. There is no relative movement between plate and shaft as far as rotational movement is concerned.
Both have the same rotational movement due to splines provided on the shaft. The flywheel is mounted on the engine crankshaft and rotates with it.
The pressure plate is bolted to the flywheel through clutch springs. It can slide freely along the axis of the clutch shaft.
The clutch is engaged due to the force exerted by the clutch springs. This force causes contact between the pressure plate, clutch plate, and the flywheel.
The clutch plate is located between the flywheel and pressure plate. The clutch plate is provided with friction material on both sides.
The rotary movement from the flywheel is transferred to the clutch plate and the clutch shaft due to friction. The clutch shaft also acts as the output shaft.
When the clutch pedal is pressed the clutch is ‘disengaged.’ The pressure plate moves back against the force of springs, and the clutch plate becomes free between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
Thus, the flywheel continues to rotate as long as the engine runs but the speed of the clutch plate declines and becomes zero. In this situation, motion is not transferred to the clutch shaft.
2. Diaphragm Spring Type Single Plate Clutch.
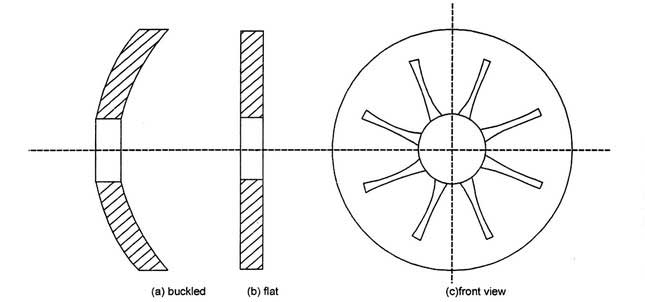
In this type of clutch, the helical springs are replaced by a single diaphragm spring which is a saucer-shaped disc. The disc is provided with profile as shown in the below figure.
The disc adopts flat shape when the clutch is engaged. In the disengaged position, the disc adopts a buckled shape as shown.
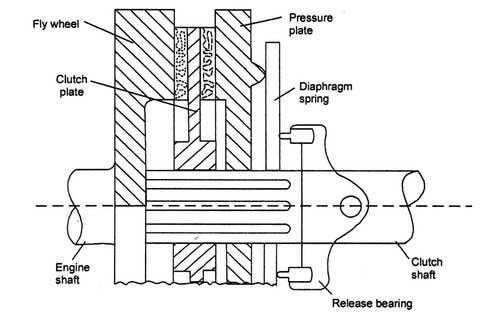
Below figure represents a simplified view of the clutch assembly.
The view shows the clutch in the ‘engaged’ position. The diaphragm spring exerts the force on the pressure plate, which causes the contact between the pressure plate, clutch plate, and flywheel.
When force is applied through the clutch pedal, the diaphragm spring is buckled and contact between pressure plate, clutch plate and flywheel is lost. The clutch is ‘disengaged,’ and motion from the flywheel is not transferred to the clutch shaft.
What is Multi Plate Clutch?
A clutch having more than one driven plate is called Multi Plate Clutch.
Some times, a single clutch plate can not transfer the required motion. This may be due to less friction force. The friction force can be increased by increasing the area of contact.
This increases the size of the clutch, and due to limited space available; it may be challenging to increase the size.
Therefore to increase the area of contact, the number of clutch plates is increased. The constructional details of the multi plate clutch are represented in the below figure.
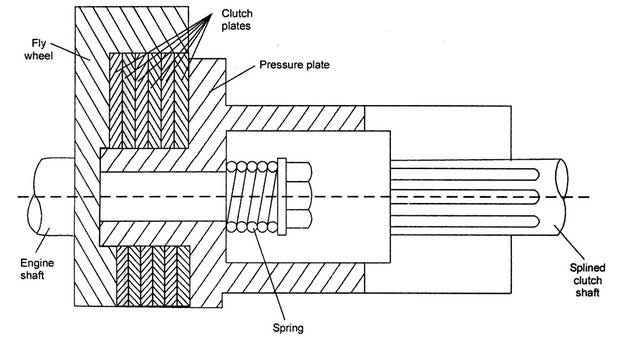
To simplify the figure, the mechanism to engage and disengage the clutch has not been shown. Internal splines are provided on the flywheel. The clutch shaft is provided with splines.
The clutch plates are assembled and are firmly pressed, with the help of pressure plate, by coil springs. These coil spring exert axial force, due to which there is contact between the clutch plates, flywheel, and the pressure plate.
The frictional surfaces on both the sides of plates help to transfer the motion from flywheel to the clutch shaft.
This is the ‘engaged’ position of the multi plate clutch.
By operating the clutch pedal, the force is exerted against the force of springs and contact between the flywheel, clutch plates, and pressure plate is lost, and no motion is transferred from flywheel to clutch shaft.
This is ‘disengaged’ position for the multi plate clutch.
Presently, in all the automobiles multi plate clutches are being used.
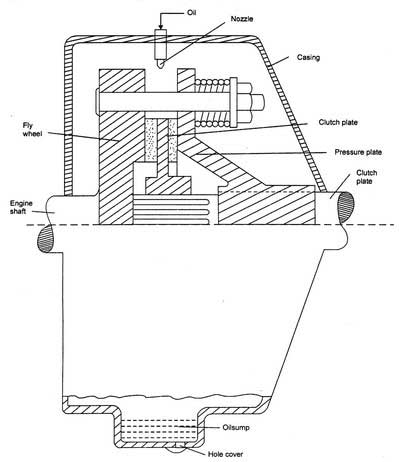
A wet clutch is a variant of the friction clutch. Here oil is sprayed on the plates with the help of nozzle. These are used in a variety of automobiles.
The friction material used on clutch plates should have a higher coefficient of friction, and these are perforated so that oil can pass through these.
These clutches have intake for oil. A sump is provided at the bottom to collect the oil from where it is drained out.
These types of clutches have a longer life than dry clutches due to better dissipation of heat.
Difference Between Dry Clutch and Wet Clutch.
The difference between dry and wet clutches is as follows:
Dry Clutch;
1. Dry clutch has a higher coefficient of friction.
2. The coefficient of friction for dry operation is 0.3 or more.
3. The torque capacity of dry clutch is high compared to a wet clutch of the same dimensions.
4. For the dry clutch, it is necessary to prevent contamination due to moisture or nearby lubricated machinery, by providing seals.
5. Heat dissipation is more difficult in dry clutches.
6. The rate of wear is far more in dry clutches compared to wet clutches.
7. The engagement in the dry clutch is rough than in case of a wet clutch.
Wet Clutch;
1. In wet clutches, the coefficient of friction is reduced due to oil.
2. The coefficient of friction is 0.1 or less for wet operation
3. The torque capacity of a wet clutch is low compared with a torque capacity of a dry clutch of same dimensions.
4. Preventing of contamination due to moisture or nearby lubricated machinery is not necessary in wet clutches.
5. In wet clutches, the lubricating oil carries away the frictional heat.
6. The rate of wear is far less in wet clutches compared to dry clutches. The wear rate in wet clutches is about 1% of the rate expected in dry clutches.
7. In wet clutches, the clutch facings are grooved to provide passage for lubricant. This reduces the net face area for transmitting torque.
Construction and Working of Multi Plate Clutch.
A multi-plate clutch is provided with more than one friction plate. In fact, in this clutch, there are two pressure plates and two friction plates, as shown in the below figure.
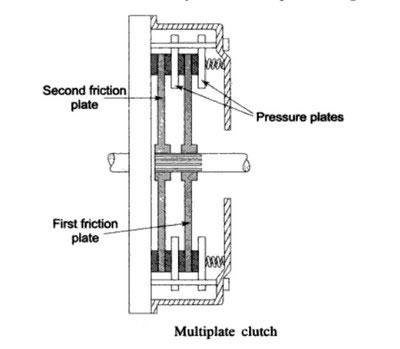
These pressure plates are linked to the clutch cover by means of studs. This clutch cover is fitted to the flywheel.
One friction plate is placed between the first and second pressure plate, and the other one is between the second pressure plate and the flywheel.
The link mechanism is the same as the one used in the single plate clutch. The two friction plates are connected to the clutch shaft using a spline arrangement.
While the flywheel is rotating, the pressure plates rotate and press against the friction plate. This causes the friction plates and thus the clutch shaft to rotate as well.
When the pedal is pressed, the flywheel continues to rotate, but the friction plates are released. This happens because they are not fully pressed by the pressure plates.
Thus, the clutch shaft also stops rotating.
Advantages of Multi Plate Clutch.
1. The number of friction surfaces increases the capacity of the clutch to transmit torque, though the size remains fixed.
Therefore, considering the same torque transmission, the overall diameter of the multi plate clutch is reduced when compared to a single plate clutch.
2. Due to this advantage, this type of clutch is used in some heavy transport vehicles and racing cars.
3. This multi plate clutch is used in scooters and motorcycles where there is limited space.